Summary of PM2.5 Pollution and Meteorology Forecast for Today at the state-level (more resources here)
Guwahati, the largest city in the North-East region, lies on the south bank of the Bhramaputra river in Assam and the city is expanding to the north of the banks. The Guwahati Municipal Corporation and the Guwahati Metropolitan Development Authority (GMDA) is the planning and development body of the greater Guwahati Metropolitan Area.
The southern corridor towards Shillong is a busy commercial area which has spawned much residential and commercial development. The western corridor houses the railroad towards the rest of India as well as several ports and jetties with access to the Bhramaputra waterway and is also where the Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi (LGB) International Airport which serves as the main gateway via air to the rest of the country. The eastern corridor connects the city centre to the Guwahati Refinery and residential areas surrounding it.
Industry contributes a substantial share to the city’s economy. Assam is one of the highest tea-producing areas in the world, contributing 80% of India’s export and 55% of the country’s total tea production. Covering an area of ~325 square kilometers, it is one of the fastest growing cities in India. Estimates suggest Guwahati will house >3 million residents by 2025. Interestingly Guwahati is not the official capital of Assam, the capital is Dispur which is a locality at the southern part of the city.
To assess Guwahati’s air quality, we selected an airshed covering 40km x 30km. This domain is further segregated into 1km grids, to study the spatial variations in the emission and the pollution loads.
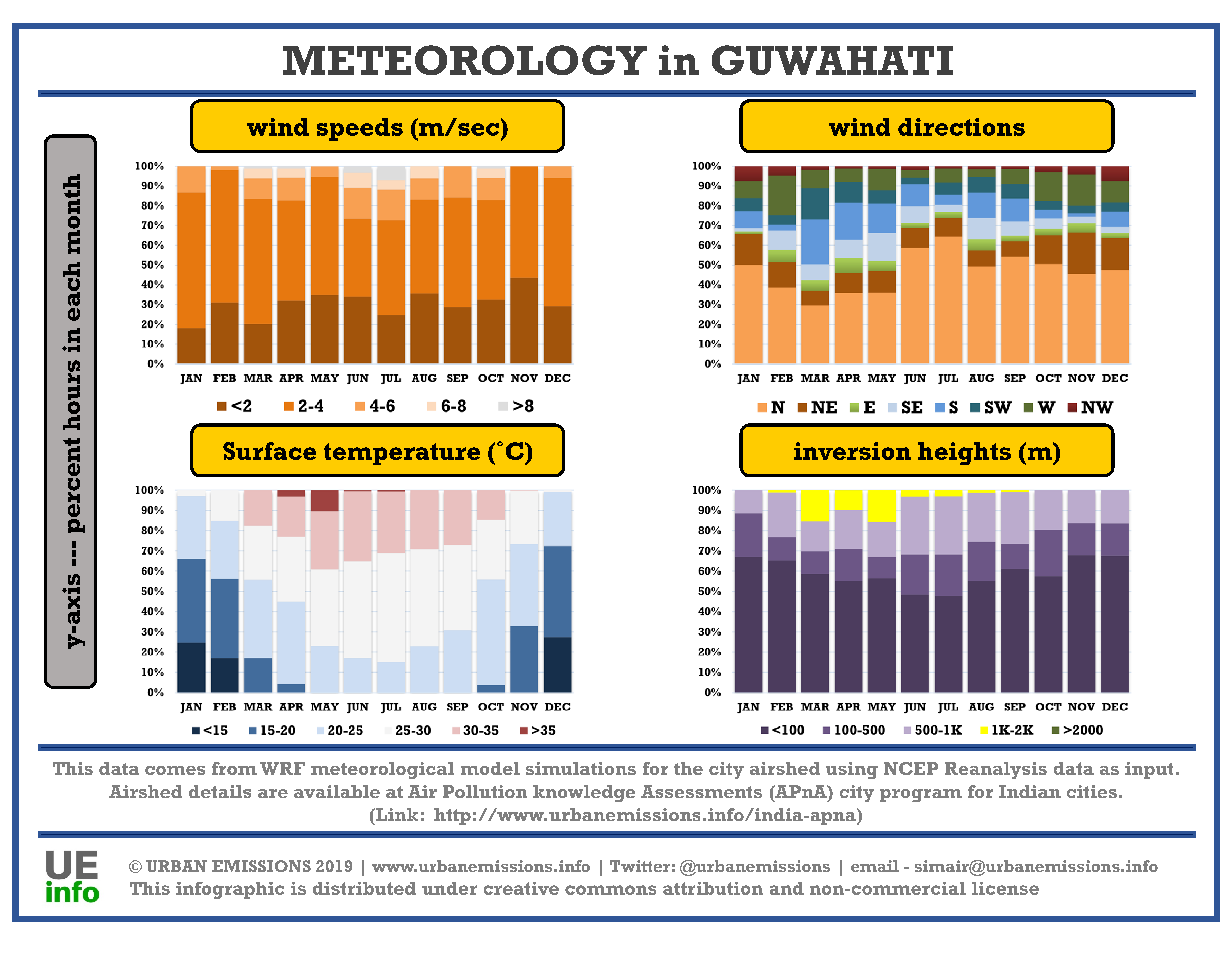
Meteorology fields are important as they have a direct impact on air pollution concentrations. During periods of high precipitation or high speed winds, emissions from a city are swept away and do not have an impact on concentrations. On the other hand, during the winter months when temperatures and inversion heights are low, there is a greater impact of emissions on pollution concentrations. Low temperatures also affect behaviour through the need for space and water heating – which in turn has increases emissions.
We processed the NCEP Reanalysis global meteorological fields from 2010 to 2018 through the 3D-WRF meteorological model. A summary of the data for one year, averaged for the city’s airshed is presented below by month. Download the processed data which includes information on year, month, day, hour, precipitation (mm/hour), mixing height (m), temperature (C), wind speed (m/sec), and wind direction (degrees) – key parameters which determine the intensity of dispersion of emissions.
Multi-Pollutant Emission Inventory
We compiled an emissions inventory for the Guwahati region for the following pollutants – sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), non-methane volatile organic compounds (NMVOCs), carbon dioxide (CO2); and particulate matter (PM) in four bins (a) coarse PM with size fraction between 2.5 and 10 μm (b) fine PM with size fraction less than 2.5 μm (c) black carbon (BC) and (d) organic carbon (OC), for year 2015 and projected to 2030. In Phase 1, base year for all the calculations was 2015. In Phase 2, all the calculations are updated for year 2018.
 We customized the SIM-air family of tools to fit the base information collated from disparate sources. Apart from the official reports, resource material ranges from GIS databases of land use, land cover, roads and rail lines, water bodies, built up area (represented in the adjacent figure), commercial activities (such as hotels, hospitals, kiosks, restaurants, malls, cinema complexes, traffic intersections, worship points, industrial hubs, and telecom towers), to population density and meteorology at the finest spatial resolution possible (1-km). A detailed description of these resources is published as a journal article in 2019, which also includes a summary of baselines and pollution analysis for 20 Indian cities.
We customized the SIM-air family of tools to fit the base information collated from disparate sources. Apart from the official reports, resource material ranges from GIS databases of land use, land cover, roads and rail lines, water bodies, built up area (represented in the adjacent figure), commercial activities (such as hotels, hospitals, kiosks, restaurants, malls, cinema complexes, traffic intersections, worship points, industrial hubs, and telecom towers), to population density and meteorology at the finest spatial resolution possible (1-km). A detailed description of these resources is published as a journal article in 2019, which also includes a summary of baselines and pollution analysis for 20 Indian cities.
This emissions inventory is based on available local activity and fuel consumption estimates for the selected urban airshed (represented in the grid above). This information is collated from multiple agencies ranging from the central pollution control board, state pollution control board, census bureau, national sample survey office, ministry of road transport and highways, annual survey of industries, central electrical authority, ministry of heavy industries, and municipal waste management, and publications from academic and non-governmental institutions.
For the road transport emissions inventory, besides the total number of vehicles and their usage information, we also utilized vehicle speed information to spatially and temporally allocate the estimated emissions to the respective grids. This is a product of google maps services. For the city of Guwahati, we extracted the speed information for representative routes across the city for multiple days. This data is summarized below for a quick look.
 |
Click here for gridded anime |
Industry contributes a substantial share to the economy of the city. The Guwahati Refinery that processes petroleum is the most important manufacturing industry in the city. The refinery is run by the Indian Oil Corporation at a capacity of about 1 million metric tons per annum. It produces various products and supplies them to the other northeast states and also beyond to Siliguri through the Guwahati-Siliguri pipeline. The various products produced by the refinery include Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), Kerosene Oil, Turbine Fuel (aviation use), Motor Spirit, High Speed Motor Diesel, Light Diesel Oil and Raw Petroleum Coke. There is also an LPG bottling plant, a cement manufacturing and a fertilizer manufacturing facility close to the city .
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The summary for a city’s emissions inventory does not include natural emission sources (like dust storms, lightning, and seasalt) and seasonal open (agricultural and forest) fires. However, these are included in the overall chemical transport modeling in the national scale simulations. These emission sources are accounted in the concentration calculation as an external (also known as boundary or long-range) contribution to the city’s air quality.
Projections to 2030 under the business as usual scenario are influenced by the city’s social, economic, landuse, urban, and industrial layout and hence the projected (increasing and decreasing) rates that we assume are an estimate only. We based the vehicle growth rate on the sales projection numbers; industrial growth on the gross domestic product of the state; domestic sector, construction activities, brick demand, diesel usage in the generator sets, and open waste burning on population growth rates and notes from the municipalities on plans to implement waste management programs. We used these estimates to evaluate the trend in the total emissions and their likely impact on ambient PM2.5 concentrations through 2030.
The emissions inventory was then spatially segregated at a 0.01° grid resolution in longitude and latitude (equivalent of 1 km) to create a spatial map of emissions for each pollutant (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NOx, CO and VOCs). The gridded PM2.5 emissions and the total (shares by sector) emissions are presented below.
Gridded PM2.5 Emissions (2018 and 2030)
 |
 |
Total PM2.5 Emissions by Sector 2018-2030
 |
 |
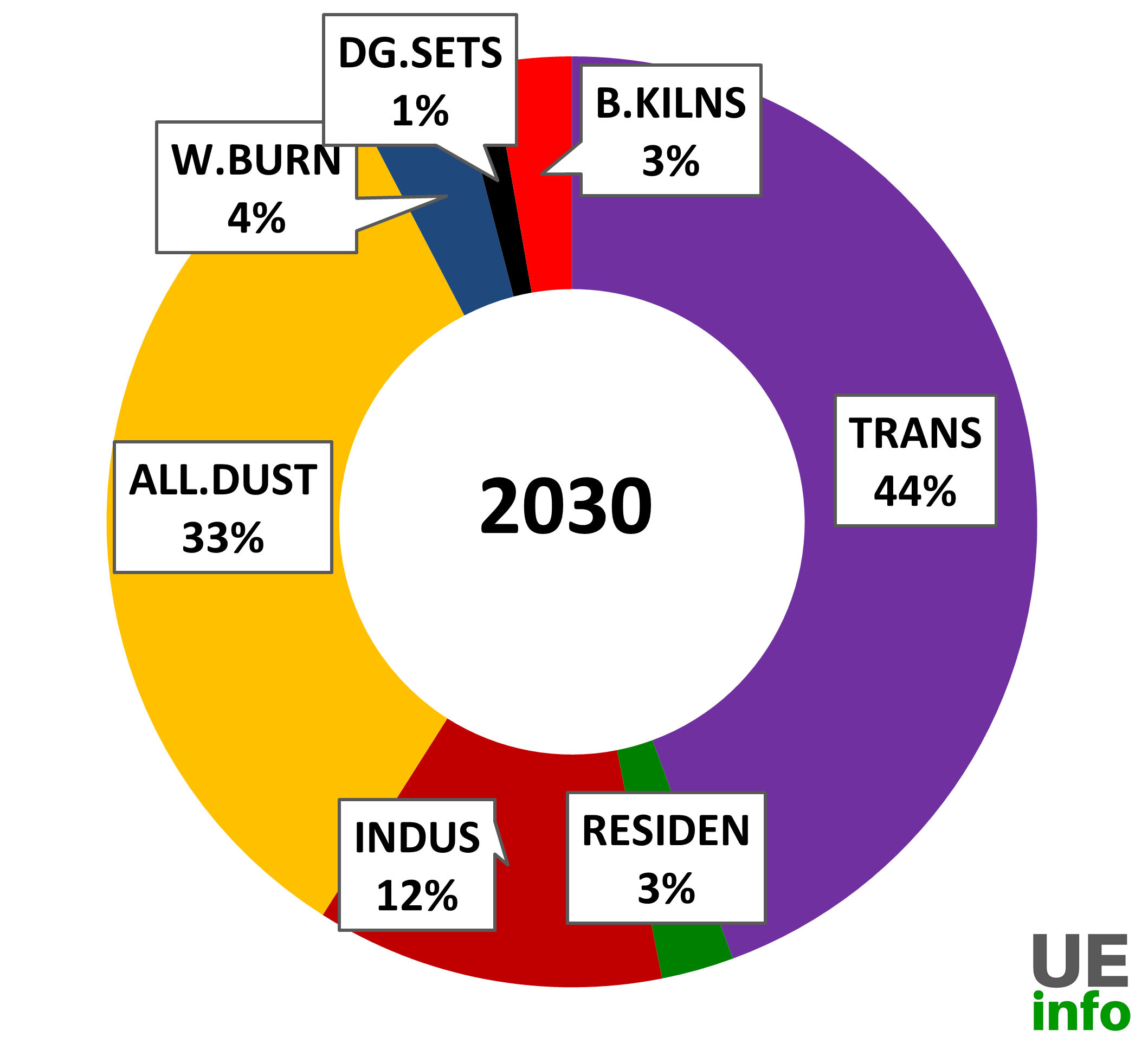 |
TRANS = transport emissions from road, rail, aviation, and shipping (for coastal cities); RESIDEN = residential emissions from cooking, heating, and lighting activities; INDUS = industrial emissions from small, medium, and heavy industries (including power generation); ALL.DUST = dust emissions from road re-suspension and construction activities; W.BURN = open waste burning emissions; DG.SETS = diesel generator set emissions; B.KILNS = brick kiln emissions (not included in the industrial emissions)
Total Estimated Emissions by Sector for 2018 (units – tons/year)
| Guwahati | PM2.5 | PM10 | BC | OC | NOx | CO | VOC | SO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transport emissions from road, rail, aviation, and shipping (for coastal cities) | 5,250 | 5,550 | 2,150 | 1,700 | 24,000 | 168,550 | 32,300 | 450 |
| Residential emissions from cooking, heating, and lighting activities | 1,100 | 1,150 | 200 | 600 | 200 | 16,800 | 2,000 | 100 |
| Industrial emissions from small, medium, and heavy industries (including power generation) | 2,150 | 2,450 | 450 | 300 | 6,800 | 3,750 | 750 | 2,300 |
| Dust emissions from road re-suspension and construction activities | 4,700 | 30,600 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Open waste burning emissions | 850 | 900 | 50 | 500 | - | 4,000 | 800 | - |
| Diesel generator set emissions | 250 | 250 | 100 | 50 | 1,550 | 5,000 | 2,250 | 50 |
| Brick kiln emissions (not included in the industrial emissions) | 650 | 650 | 200 | 250 | 600 | 8,000 | 950 | 200 |
| 14,950 | 41,550 | 3,150 | 3,400 | 33,150 | 206,100 | 39,050 | 3,100 |
Chemical Transport Modeling
We calculated the ambient PM2.5 concentrations and the source contributions, using gridded emissions inventory, 3D meteorological data (from WRF), and the CAMx regional chemical transport model. The model simulates concentrations at 0.01° grid resolution and sector contributions for the urban area, which include contributions from primary emissions, secondary sources via chemical reactions, and long range transport via boundary conditions (represented as “boundary” in the pie graph below).
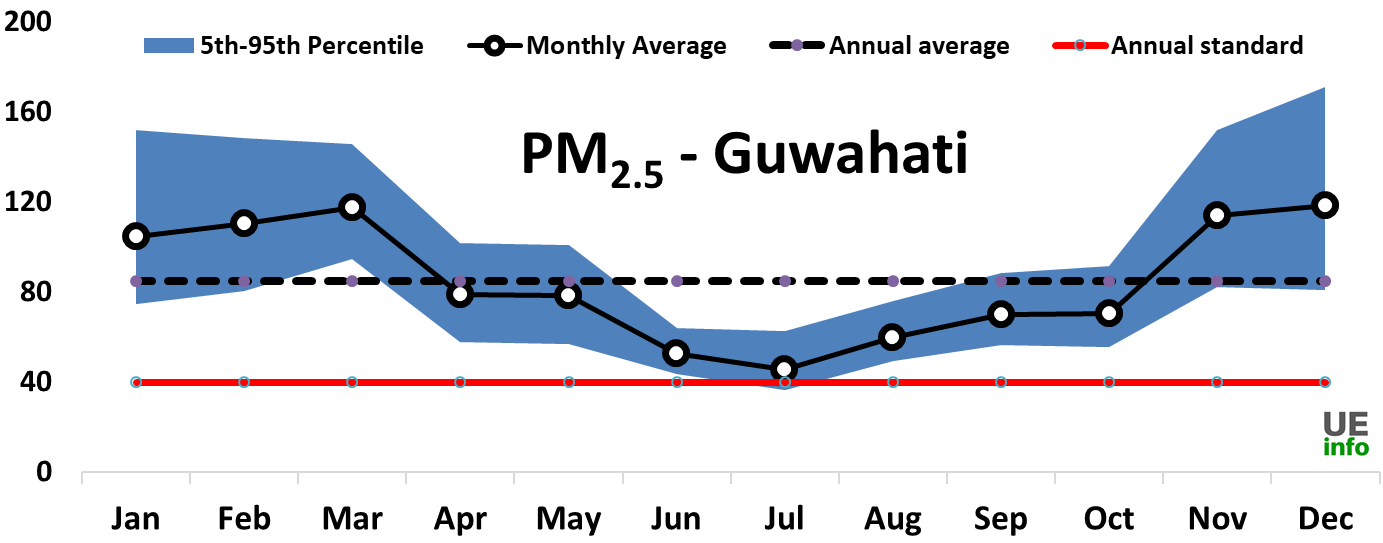
The ribbon graph shows the variation for average PM2.5 pollution by month. Due to precipitation during the monsoon, usually pollution levels dip and may fall within national air pollution standards, however most cities are unable to attain these standards at other times of the year.
The following is a map of annual average PM2.5 pollution for the city of Guwahati. The main sources contributing towards PM2.5 in 2018 are in the pie-chart on the left. The change in contributions in 2030 from different sources are shown on the right.
 |
 |
 |
There is a temporal variation in source contributions and spatial contributions depending on meteorological factors. We have a map of monthly average PM2.5 levels as well as their source contributions for every month in the charts below.
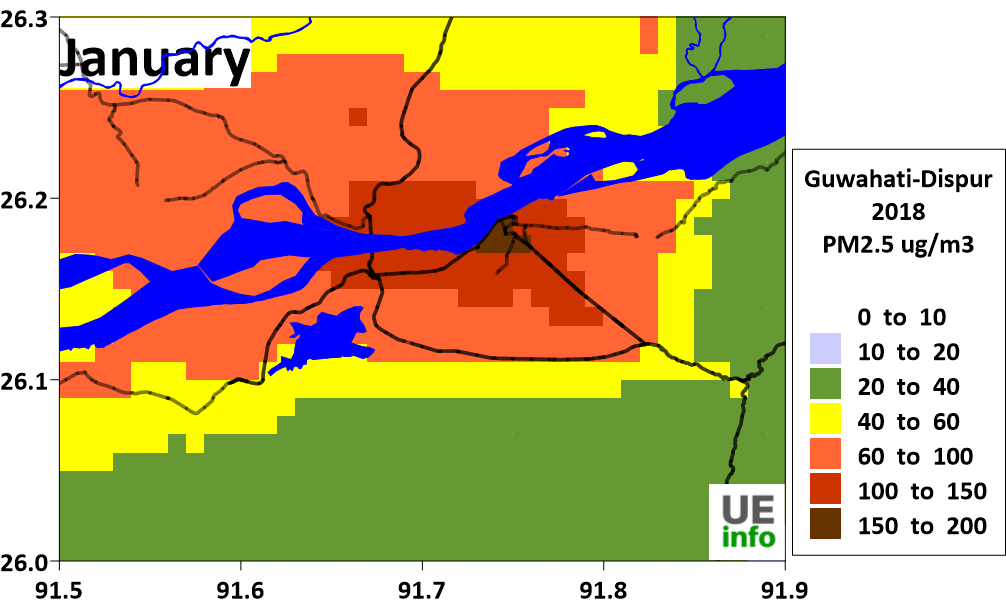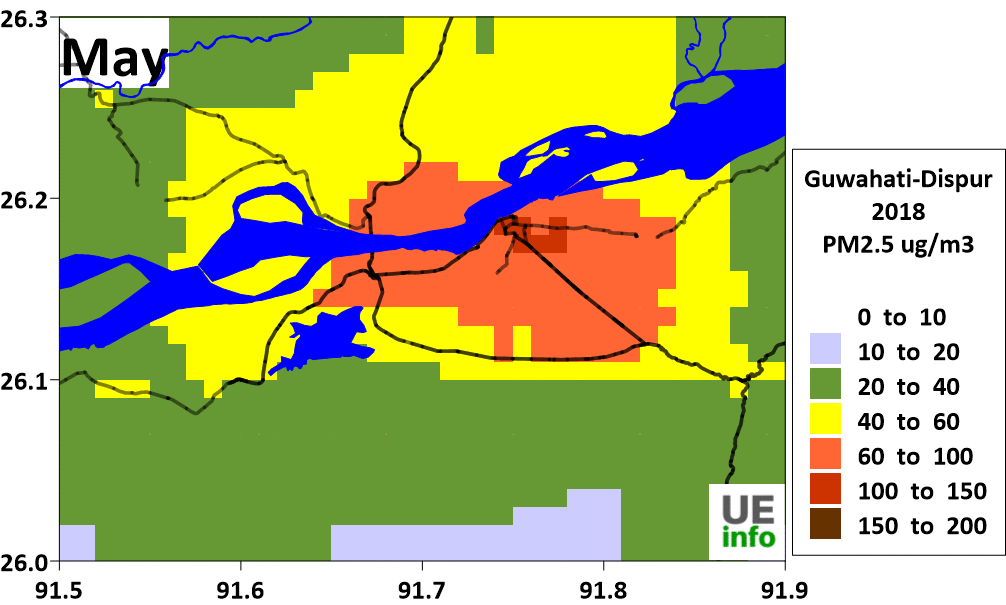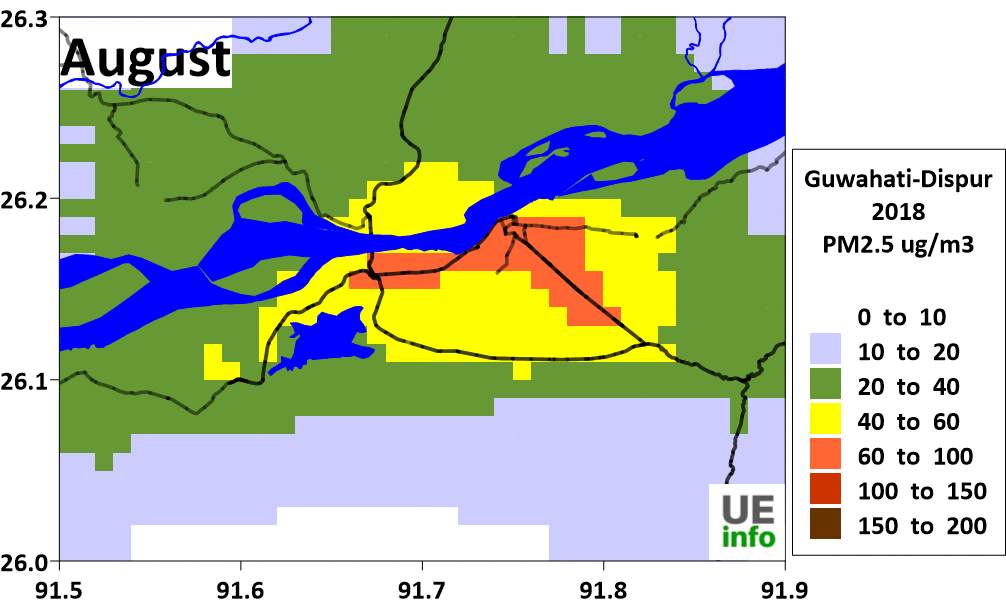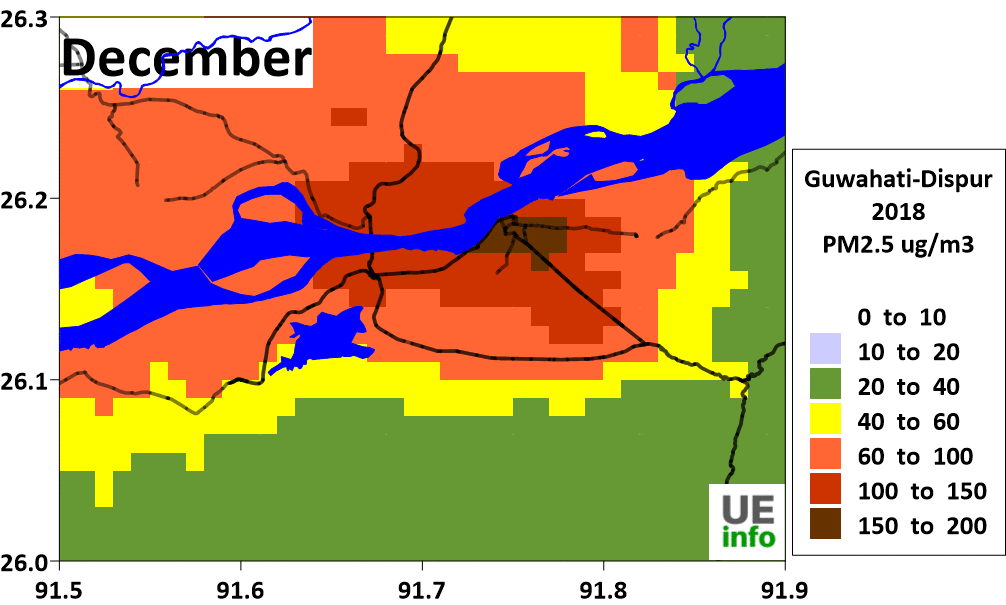 |
 |
Satellite Data Derived Surface PM2.5 Concentrations
The results of satellite data derived concentrations are useful for evaluating annual trends in pollution levels and are not a proxy for on-ground monitoring networks. This data is estimated using satellite feeds and global chemical transport models. Satellites are not measuring one location all the time, instead, a combination of satellites provide a cache of measurements that are interpreted using global chemical transport models (GEOS-Chem) to represent the vertical mix of pollution and estimate ground-based concentrations with the help of previous ground-based measurements. The global transport models rely on gridded emission estimates for multiple sectors to establish a relationship with satellite observations over multiple years. These databases were also used to study the global burden of disease, which estimated air pollution as the top 10 causes of premature mortality and morbidity in India. A summary of PM2.5 concentrations for the period of 1998 to 2016 for the city of Guwahati is presented below. The global PM2.5 files are available for download and further analysis @ Dalhousie University.
The graphs for other district PM2.5 concentrations for this period, maps of national averages, and year-wise changes are available here. The data for district level PM2.5 concentrations for 1998-2016 period for can downloaded here.
Monitoring
We present below a summary of the ambient monitoring data available under the National Ambient Monitoring Program (NAMP), operated and maintained by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB, New Delhi, India). In Guwahati, as of November 2018, there are 0 continuous and 2 manual air quality stations in operation. An archive of all the data from the NAMP network from stations across India for the period of 2011-2015 is available here.
 |
 |
 |
Resource Material
- ENVIS Centre, Assam (Link)
- Pollution Control Board, Assam (Link)
- Guwahati Municipal Corporation (Link)
- Guwahati Development Department Master Plan 2025 (Link)
- Guwahati Smart City Proposal (Link)
- CPCB repository of continuous air monitoring data (Link)
- “Assessment of PM2.5 and PM10 over Guwahati in Brahmaputra River Valley: Temporal evolution, source apportionment and meteorological dependence”, Tiwari, S. et. al. (2016) (Journal Article Link)
- “Street dust bound PAHs, carbon and heavy metals in Guwahati city – Seasonality, toxicity and sources”, Hussain, K. et. al. (2015) (Journal Article Link)
- “Concern over poor air quality and traffic congestion in north east cities; action must gather momentum”, Centre for Science and Environment. Media Briefing Workshop Press Release. (2013) (Link)
- “Performance Audit of the Greater Guwahati area with special emphasis on the role of the Pollution Control Board, Assam”, Report of the Comptroller and Auditor General of India: Government of Assam. (Report No. 3 of 2016) .Pages vii – ix, 5-7 and 21 – 32. (Link)
Back to the APnA page.
All the analysis and results are sole responsibility of the authors @ UrbanEmissions.Info. Please send you comments and questions to simair@urbanemissions.info